 |
Basic Guide to
DOS
Logon to MS-DOS |
Command Prompt
You can access DOS
from any Windows9.x system (Win95,98)
You have two options, either restart your computer
in MS-DOS mode by pressing on Start>>Shut Down and
selecting Restart in MS-DOS mode
or simply clicking MS-DOS Prompt icon located in
the Start menu (Start>>Programs)
MS-DOS Prompt simply simulates DOS while still
running Windows.
Type "exit" and you will return to
Windows.
If you restarted your computer in MS-DOS mode and
typed "exit" you will have to wait
for Windows to load again...
In this tutorial we will be using MS-DOS Prompt
because we still want to access stuff in Windows.
To gain quick access to DOS go to Run box and
type "command"
a black box will open with the following
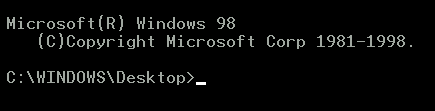
To get more comfortable press on Full screen icon
You can always switch back by pressing ALT+<enter>
on your keyboard.
What you're seeing now is called the Command
Prompt,
this is where you type commands for DOS to
execute.
DOS requires a lot of typing rather than mouse
clicking.
The "command" keyword you've just typed
inside Run box refers
to DOS Command interpreter called command.com
Many computer users think that "command.com"
is the actual DOS program,
so they carry it with them and discover that it
doesn't work on a computer without DOS.
Command.com is not the actual DOS, it's an
interface between you
and DOS that translates
the commands you type at the Prompt into
a
language "understood" by the computer.
For completeness, the actual DOS program is IO.SYS
located at the root directory (Drive C:)
IO.SYS is a hidden file, you won't be able to see
it in Windows unless you unhide all files in the root directory.
|
|
 |
Choose a Tutorial
What do you need ?
|

